Hypothyroidism: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
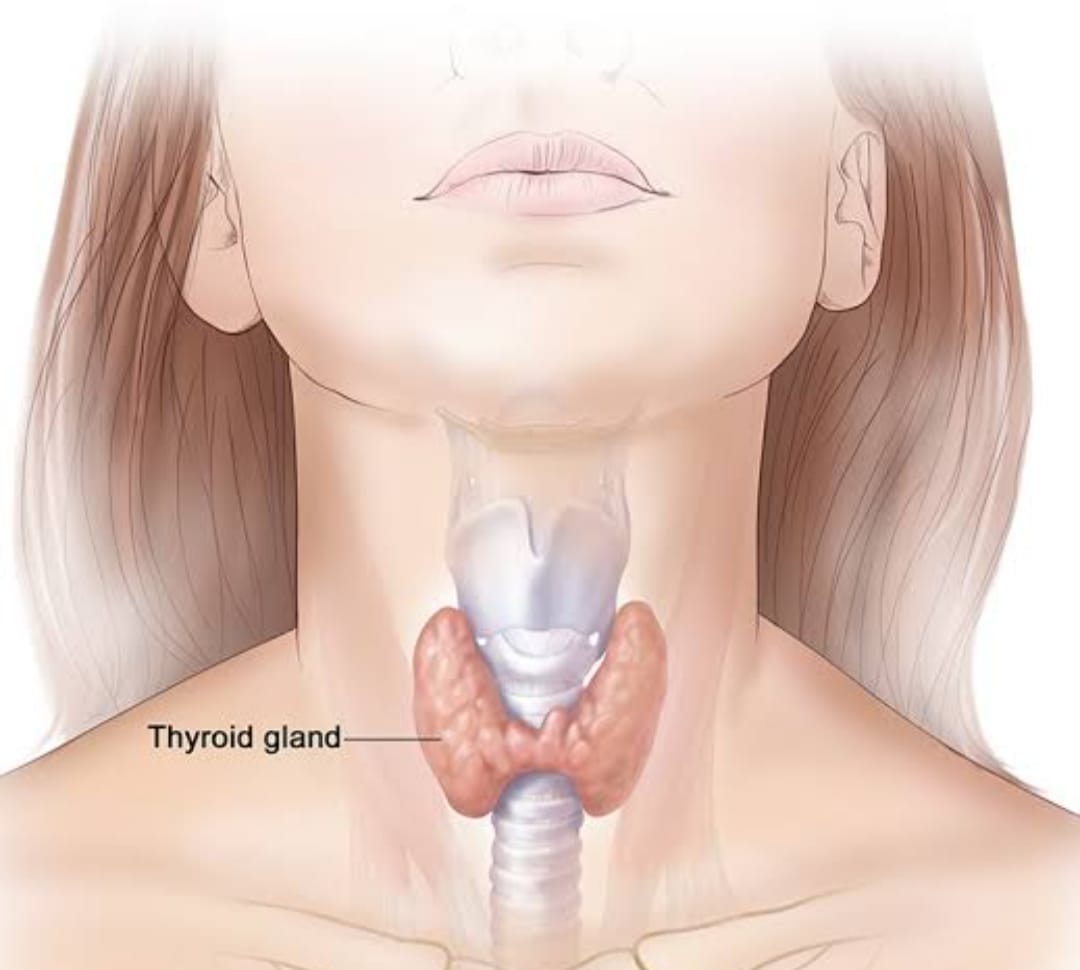
Hypothyroidism is a medical condition characterized by an underactive thyroid gland, which fails to produce enough thyroid hormones to meet the body’s needs.This makes your metabolism slow down. The thyroid gland, located in the front of the neck, plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism, energy production, and various bodily functions.
Alternative Names
Adult hypothyroidism; Underactive thyroid; Goiter – hypothyroidism; Thyroiditis – hypothyroidism; Thyroid hormone – hypothyroidism; Myxedema.
Causes of Hypothyroidism
- Many elements are responsible for causing hypothyroidism issues.
- Autoimmune is a disease caused by the immune system,
- Because of inflammation of the thyroid gland from Hashimoto’s disease,
- Because of radiation therapy for cancer,
- If the thyroid has been surgically removed,
- Hyperthyroidism, due to the treatment of thyroid problems,
- Also side effects of certain medications can cause hypothyroidism.
Symptoms
Early symptoms:
- Thin, brittle hair or fingernails
- Weakness
- Weight gain
- Hard stools or constipation
- Feeling cold
- Fatigue or feeling slowed down
- Heavier and irregular menstrual periods
- Joint or muscle pain
- Whiteness or dry skin
- Sadness or depression
Late symptoms, if untreated:
- Slow pulse
- Decreased taste and smell
- Dryness
- Puffy face, hands, and feet
- Slow speech
- Thickening of the skin
- Thinning of eyebrows
- Low body temperature
When to see a doctor
Visit to a doctor if you have symptoms of hypothyroidism.
If you are being treated for hypothyroidism, call your doctor if:
- You develop chest pain or rapid heartbeat
- Your symptoms get worse or do not improve with treatment
- You develop new symptoms
Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH):
Normal range: 0.4 to 4.0 milli-international units per liter (mIU/L)
Free Thyroxine (FT4):
Normal range: 0.8 to 1.8 nanograms per deciliter (ng/dL) or 10 to 23 picomoles per liter (pmol/L)
Diagnosis in Hypothyroidism
The doctor will do a physical test and may find the symptoms mentioned above.
Blood tests are also ordered to measure your thyroid hormones TSH and T4.
Specialized thyroid tests like thyroid peroxidase antibodies may be needed.
You may also have tests to check:
- Cholesterol levels
- Complete blood count (CBC)
- Liver enzymes
- Prolactin
- Sodium
- Cortisol
Treatment
Treatment is aimed at replacing the thyroid hormone you are lacking.
Levothyroxine is the most commonly used medicine:
- You will be prescribed the lowest dose possible that relieves your symptoms and brings your blood thyroid hormone levels back to normal.
- If you have heart disease or you are older, your provider may start you on a very small dose.
- Most people with an underactive thyroid will need to take this medicine for life.
- Levothyroxine is usually a pill, but some people with very severe hypothyroidism first need to be treated in the hospital with intravenous levothyroxine (given through a vein).
- When starting you on your medicine, your provider may check your hormone levels every 2 to 3 months. After that, your thyroid hormone levels should be monitored at least once every year.
When you are taking thyroid medicine, be aware of the following:
Do not stop taking the medicine, even when you feel better. Continue taking it exactly as your provider prescribed.
- If you change brands of thyroid medicine, let your provider know. Your levels may need to be checked.
- What you eat can change the way your body absorbs thyroid medicine. Talk with your provider if you are eating a lot of soy products or are on a high-fiber diet.
- Thyroid medicine works best on an empty stomach and when taken 1 hour before any other medicines. Ask your provider if you should take your medicine at bedtime. Taking it at bedtime may allow your body to absorb the medicine better than taking it in the daytime.
- Wait at least 4 hours after taking thyroid hormone before you take fiber supplements, calcium, iron, multivitamins, aluminum hydroxide antacids, colestipol, or medicines that bind bile acids.
- While you are taking thyroid replacement therapy, tell your provider if you have any symptoms that suggest your dose is too high, such as:
- Anxiety
- Palpitations
- Rapid weight loss
- Restlessness or shakiness (tremors)
- Sweating
What to eat?
Patients suffering from hypothyroidism should eat a balanced diet containing nutrients supplements as fibres, proteins, vitamins and minerals. For this, the diet should include grains, pulses, green leafy vegetables, various fruits, milk and milk products, meat, fish, eggs.
Nutrients like vitamin B12, iodine, selenium, zinc, probiotics are vital in the diet of hypothyroidism patients. Vitamin-B12 is abundant in milk, eggs, meat, fish, sesame. Apart from this, the probiotics present in yogurt are also useful. So include curd too.
What food to avoid?
Hypothyroidism is more likely to increase weight and increase blood cholesterol. For this, you try not to eat eat fatty foods, oily foods, sugary sweet foods, bakery products, fast food, junk food.
You may also interested in:
Beetroot A Hidden Gem of Health Benefits You Shouldn’t Ignore
All you need to know about Sleep apnea
